Peanuts have a very important Iron content that must be considered by every individual who has a healthy diet, particularly vegetarians, vegans, and individuals with anemia. Peanuts are not a snack; it is a functional food that has high nutrient density and promotes total well-being. It is important to understand the amount of Iron in peanuts, especially in every 100g, and how it compares with other nuts in order to achieve the best intake of Iron by using plant-based foods.
Mineral Profile of Peanuts: Iron and More
Peanuts are considered a small source of minerals. As stated by the USDA National Nutrient Database, the amount of Iron in peanuts per 100g is 4.58 mg on average. This is a high value, especially since the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of Iron in adult men is about 8 mg and in adult women, 18 mg. Peanuts are a healthy choice of the mineral profile, i.e.:
| Principle | Nutrient Value (per 100g) | % of RDA |
| Iron | 4.58 mg | 57% |
| Magnesium | 168 mg | 42% |
| Copper | 1.144 mg | 127% |
| Zinc | 3.27 mg | 30% |
| Calcium | 92 mg | 9% |
| Manganese | 1.934 mg | 84% |
Studies show that peanuts are comfortable to supply a significant part of your mineral needs in case you consumed them regularly.
Iron Content in Pecans: Comparison and Context
A lot of users are looking for Iron content in pecans as another source of iron in Iranian nuts. Based on valid nutritional sources and USDA information:
- Every 100g of Pecans contains 2.53 mg of Iron.
This is because pecans contain approximately half of the Iron content of peanuts per 100g.
Pecans, on the other hand, contain a lot of fiber, thiamin, copper, and manganese, making them still a significant constituent of the nut family for those who are interested in the general health advantages.
Iron in Peanuts: Bioavailability and Absorption Challenges
Although the level of Iron in peanuts is good, you should know the conditions that influence absorption. Peanuts contain non-heme Iron (plant-based), which is not absorbed as effectively as heme Iron (animal-derived). A few compounds in peanuts can inhibit the absorption of Iron; these are phytates in particular and polyphenols. Research indicates that the nutrients are generally absorbed as Iron in the range of 1.8, which is considerably low as opposed to other foods, such as bread, that may absorb a maximum of 6.6.
Increasing the Iron Absorption of Peanuts
Vitamin C is the best means of enhancing the absorption of Iron content. The absorption inhibitors can be overcome by eating peanuts with fresh fruits (oranges or strawberries) or vegetables that are rich in vitamin C. Alternation of nuts with foods that do not lower Iron absorption is also beneficial, e.g. animal proteins or citrus.
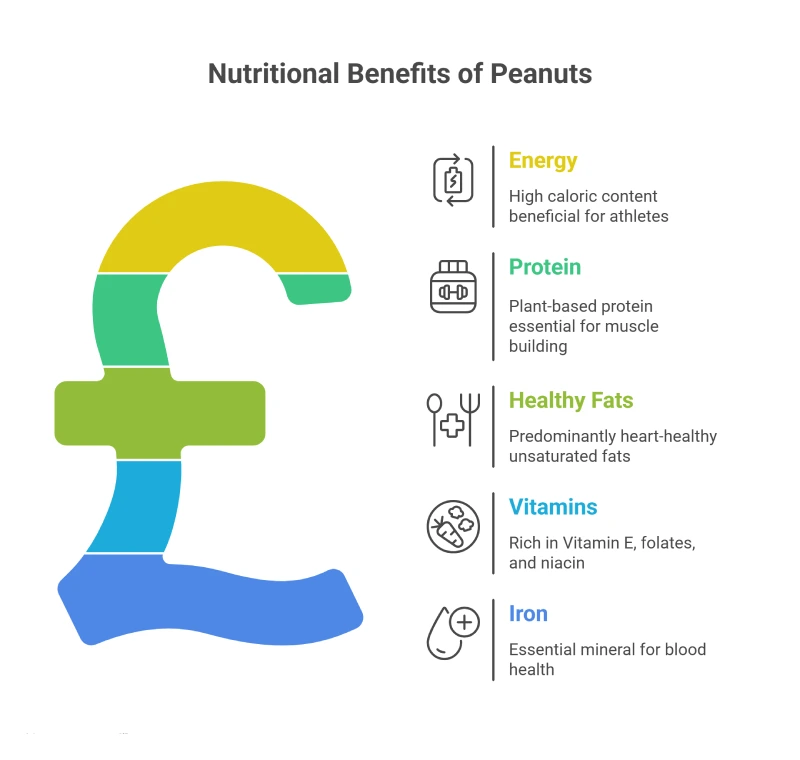
Nutritional Benefits of Peanuts
Peanuts are not only a matter of mineral content; they are energy-filled and full of plant-based compounds beneficial to the human body. More than Iron content in peanuts, nutritional value per 100g contains:
- 567 kcal (high energy, beneficial to athletes)
- 80 g protein (plant-based)
- 24 grams total fat, which is predominantly heart-healthy unsaturated fat.
- Vitamin E, folates, niacin, and so on.
Read More: benefits of peanuts
A combination of all these nutrients, combined with Iron, makes peanuts a functional food, or one that provides more than essential nutrition.
Ways to Add Peanuts to Our Daily Foods
To use Iron content in peanuts, use them in these ways:
- Eat crack and snack peanuts as they are in the shell to get the traditional taste.
- Prepare your own peanut butter through the mixing of roasted peanuts with honey and a pinch of salt.
- Add peanuts to salads and oatmeal to add some crunch.
- Roll crushed peanuts over frozen bananas.
- Combine peanuts, raisins, coconuts, and chocolate chips to make trail mix.
- Add granola bars with peanuts or bake them into peanut butter cookies.
- A soft and salty snack would be boiled peanuts, a Southern delicacy.
- Serve peanut butter quickly and simply as a dip with carrots, radishes, or celery.
- Add drizzle to popcorn or to smoothies to get some unique flavors.
- Eat peanuts in savory foods such as Asian-style curry, satay sauce or stir-fries.
How Much Iron Can You Get from Peanuts in Real Diets?
In real terms, consuming 100 grams of peanuts would provide almost half of the daily recommended adult male intake of Iron as well as a quarter of the adult female intake of Iron (which is higher). The amount of Iron content in peanuts in 100g of peanuts is high in comparison with most plant foods, although the user should consider the absorption problem as indicated above.
Kourosh Foods: Commitment to Quality
Kourosh Foods is one of the largest manufacturers, suppliers, and exporters of dried fruits, nuts, raisins, and dates in Iran. It is particular to international food safety standards and affordable prices, which soon made the company a reputable one at the local and international levels. Check our website for our products and place your order today.
FAQs
- How much Iron is in 100g of peanuts?
Iron content in peanuts per 100g is around 4.58 mg. - Is the Iron in peanuts easily absorbed?
Iron from peanuts is non-heme and absorption is limited by phytates, but vitamin C can help. - How much Iron is in pecans compared to peanuts?
Pecans contain 2.53 mg of Iron/100g, while peanuts offer up to 4.58 mg/100g. - Is eating peanuts helpful for anemia?
Peanuts can support overall Iron intake, especially in vegetarian diets, but should be paired with vitamin C for the best effect. - What other minerals do peanuts provide?
In addition to Iron, peanuts supply magnesium, copper, zinc, and manganese in substantial amounts, supporting whole-body wellness.